Learn about firewalls and their role in network security. Understand different types of firewalls and how they protect against cyber threats. Explore common types of network intrusions and discover measures…
Learn Ethical Hacking -CEHv10 from scratch

This Course Ethical Hacking – CEHv10 has 95 Lessons to cover complete training with theory as well as practical demonstrations. It covers syllabus of CEH v10 Certified Ethical Hacker version 10. later part we will see CEHV10 practice question answers | practice tests — scroll down for that.
Course has been design in a way so that any beginners level to advance level of people in cyber security can easily understand and can be benefited.
Tutor is having more than 10 yrs Experience of providing training world wide.
What you’ll learn
- Cyber security
- Complete CEH v10
- Ethical hacking
- Hacking
- Information Security
- Security awareness
How many topics will be covered in Ethical Hacking – CEHv10 course ?
TOTAL OF 94 different topics you will have mastery after you finish this course!!
Part 1: CEH Introduction
Part 2: Getting Ready with Windows PC for CEH
Part 3: Installing and Updating Kali Linux
Part 4: Hacking, Hacker Types and Ethics
Part 5: Hacking Vocabulary
Part 6: Information Security
Part 7: Attack Types and Vector
Part 8: 5 Phases of Hacking
Part 9: Foot Printing and Reconnaissance
Part 10: Google Hacking
Part 11: Website Reconnaissance
Part 12: Metagoofil Metadata
Part 13: Email Recon Footprint
Part 14: whois, nslookup tool for Recon

Part 15: Scanning Network
Part 16: Port Discovery
Part 17: Stealth Idle Scan
Part 18: OS & Application Fingerprint
Part 19: Vulnerability Scanning
Part 20: Windows Vulnerability
Part 21: Network Mapping Tool
Part 22: Proxy Server
Part 23: Public Proxy Server
Part 24: Enumeration Concept
Part 25: NetBIOS Enumeration
Part 26: SNMP Enumeration
Part 27: LDAP Enumeration
Part 28: SMTP Enumeration
Part 29: System Hacking Overview
Part 30: Windows Password Break
Part 31: Password Cracking Overview
Part 32: Password Cracking Telnet/HTTP/FTP
Part 33: Rainbow crack Lab Setup
Part 34: Rainbow Crack Demonstration
Part 35: Password Reset Hacking
Part 36: DHCP Starvation Attack
Part 37: Malicious Exe Script
Part 38: Spyware
Part 39: NTFS Alt Data Streams Exploits
Part 40: Steganography with Open puff
Part 41: Steganography with snow
Part 42: Covering track after hack
Part 43: Malware Overview
Part 44: Trojan Overview and Execute
Part 45: Creating Trojan
Part 46: Virus Overview
Part 47: Creating Virus
Part 48: Detecting Malware
Part 49: Malware Analysis
Part 50: Hash file verification
Part 51: Sniffing Overview
Part 52: CAM Table overflow, Port Security
Part 53: DHCP Snooping
Part 54: Dynamic ARP Inspection
Part 55: Social Engineering
Part 56: Denial of Service Attack
Part 57: Session Hijack
Part 58: Hack Web Server
Part 59: Buffer Overflow Attack
Part 60: Shell Shock Attack
Part 61: OWASP Broken Web Application Project
Part 62: SQL Introduction
Part 63: SQL Injection
Part 64: Web App Vulnerabilities Word press
Part 65: Wireless Hacking
Part 66: Using an Android VM
Part 67: Malware for Mobile
Part 68: Mobile Device Risk and Best practices
Part 69: Firewall Evasion
Part 70: Firewall ACL Example
Part 71: NAT and PAT Fundamentals
Part 72: IDS IPS Evasion
Part 73: Honeypot
Part 74: Cloud Computing
Part 75: CIA
Part 76: Policies
Part 77: Quantifying Risk
Part 78: Separation of Duties
Part 79: Sy mmetrical Encryption Concept
Part 80: Asymmetrical Encryption Concept
Part 81: Control Types
Part 82: Multifactor Authentication
Part 83: Centralized identity Management
Part 84: Kerberos and Single sign on
Part 85: Backup and Media Management
Part 86: Operation Security Control
Part 87: Physical Security Controls
Part 88: Incident Response
Part 89: VPNs
Part 90: Disaster Recovery Planning
Part 91: Pen Testing Tips
Part 92: Useful Tools
Part 93: Case Study
Part 94: IOT
Exam Summary
| Exam Title: | Certified Ethical Hacker (ANSI) |
| Exam Code: | 312-50 (ECC EXAM), 312-50 (VUE) |
| Number of Questions: | 125 |
| Duration: | 4 hours |
| Availability: | ECCEXAM / VUE Test |
| Format: | Multiple Choice |
| Passing Score: | 70% |
| Exam Cost: | $1,199* (Included in Certify course) |
Ethical Hacking CEHV10 QUESTION AND ANSWERS | PRACTICE TESTS | Q&Q
Question 1.
_________ is a set of extensions to DNS that provide the origin authentication of DNS data to DNS clients (resolvers) so as to reduce the threat of DNS poisoning, spoofing, and similar types of attacks.
- A. DNSSEC
- B. Resource records
- C. Resource transfer
- D. Zone transfer
Answer 1. A
Question 2.
PGP, SSL, and IKE are all examples of which type of cryptography?
- A. Hash Algorithm
- B. Digest
- C. Secret Key
- D. Public Key
Answer 2. D
Question 3.
Which of the following is considered as one of the most reliable forms of TCP scanning?
- A. TCP Connect/Full Open Scan
- B. Half-open Scan
- C. NULL Scan
- D. Xmas Scan
Answer 3. A
Question 4.
Which of the following scanning method splits the TCP header into several packets and makes it difficult for packet filters to detect the purpose of the packet?
- A. ICMP Echo scanning
- B. SYN/FIN scanning using IP fragments
- C. ACK flag probe scanning
- D. IPID scanning
Answer 4. B
Question 5.
Which of the following is the BEST way to defend against network sniffing?
- A. Restrict Physical Access to Server Rooms hosting Critical Servers
- B. Use Static IP Address
- C. Using encryption protocols to secure network communications
- D. Register all machines MAC Address in a Centralized Database
Answer 5. C
Question 6.
You have successfully gained access to a Linux server and would like to ensure that the succeeding outgoing traffic from this server will not be caught by
Network-Based Intrusion Detection Systems (NIDS).
What is the best way to evade the NIDS?
- A. Out of band signaling
- B. Protocol Isolation
- C. Encryption
- D. Alternate Data Streams
Answer 6. C
Question 7.
What is the purpose of a demilitarized zone on a network?
- A. To scan all traffic coming through the DMZ to the internal network
- B. To only provide direct access to the nodes within the DMZ and protect the network behind it
- C. To provide a place to put the honeypot
- D. To contain the network devices you wish to protect
Answer 7. B
Question 8.
You need to deploy a new web-based software package for your organization. The package requires three separate servers and needs to be available on the
Internet. What is the recommended architecture in terms of server placement?
- A. All three servers need to be placed internally
- B. A web server facing the Internet, an application server on the internal network, a database server on the internal network
- C. A web server and the database server facing the Internet, an application server on the internal network
- D. All three servers need to face the Internet so that they can communicate between themselves
Answer 8. B
Question 9.
The security administrator of ABC needs to permit Internet traffic in the host 10.0.0.2 and UDP traffic in the host 10.0.0.3. He also needs to permit all FTP traffic to the rest of the network and deny all other traffic. After he applied his ACL configuration in the router, nobody can access to the ftp, and the permitted hosts cannot access the Internet. According to the next configuration, what is happening in the network?
- A. The ACL 104 needs to be first because is UDP
- B. The ACL 110 needs to be changed to port 80
- C. The ACL for FTP must be before the ACL 110
- D. The first ACL is denying all TCP traffic and the other ACLs are being ignored by the router
Answer 9. D
Question 10.
When conducting a penetration test, it is crucial to use all means to get all available information about the target network. One of the ways to do that is by sniffing the network. Which of the following cannot be performed by the passive network sniffing?
- A. Identifying operating systems, services, protocols and devices
- B. Modifying and replaying captured network traffic
- C. Collecting unencrypted information about usernames and passwords
- D. Capturing a network traffic for further analysis
Answer 10. B
Question 11.
Which tool allows analysts and pen testers to examine links between data using graphs and link analysis?
- A. Metasploit
- B. Cain & Abel
- C. Maltego
- D. Wireshark
Answer 11. C
Question 12.
A hacker is an intelligent individual with excellent computer skills and the ability to explore a computer’s software and hardware without the owner’s permission.
Their intention can either be to simply gain knowledge or to illegally make changes.
Which of the following class of hacker refers to an individual who works both offensively and defensively at various times?
- A. White Hat
- B. Suicide Hacker
- C. Gray Hat
- D. Black Hat
Answer 12. C
Question 13.
Websites and web portals that provide web services commonly use the Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP). Which of the following is an incorrect definition or characteristics of the protocol?
- A. Based on XML
- B. Only compatible with the application protocol HTTP
- C. Exchanges data between web services
- D. Provides a structured model for messaging
Answer 13. B
Question 14.
You have gained physical access to a Windows 2008 R2 server which has an accessible disc drive. When you attempt to boot the server and log in, you are unable to guess the password. In your toolkit, you have an Ubuntu 9.10 Linux LiveCD. Which Linux-based tool can change any user’s password or activate disabled Windows accounts?
- A. John the Ripper
- B. SET
- C. CHNTPW
- D. Cain & Abel
Answer 14. C
Question 15.
From the following table, identify the wrong answer in terms of Range (ft).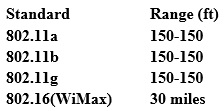
- A. 802.11b
- B. 802.11g
- C. 802.16(WiMax)
- D. 802.11a
Answer 15. D
Question 16.
You are doing an internal security audit and intend to find out what ports are open on all the servers. What is the best way to find out?
- A. Scan servers with Nmap
- B. Scan servers with MBSA
- C. Telnet to every port on each server
- D. Physically go to each server
Answer 16. A
Question 17.
Which Intrusion Detection System is the best applicable for large environments where critical assets on the network need extra scrutiny and is ideal for observing sensitive network segments?
- A. Honeypots
- B. Firewalls
- C. Network-based intrusion detection system (NIDS)
- D. Host-based intrusion detection system (HIDS)
Answer 17. C
Question 18.
Which of the following is a serious vulnerability in the popular OpenSSL cryptographic software library? This weakness allows stealing the information protected, under normal conditions, by the SSL/TLS encryption used to secure the Internet.
- A. SSL/TLS Renegotiation Vulnerability
- B. Shellshock
- C. Heartbleed Bug
- D. POODLE
Answer 18 C
————————————————————————————————————————————
Agile project management Artificial Intelligence aws blockchain cloud computing coding interview coding interviews Collaboration Coursera css cybersecurity cyber threats data analysis data breaches data science data visualization devops django docker excel flask Grafana html It Certification java javascript ketan kk Kubernetes machine learning machine learning engineer Network & Security nodejs online courses online learning Operating Systems Other It & Software pen testing Project Management python Software Engineering Terraform Udemy courses VLAN web development











